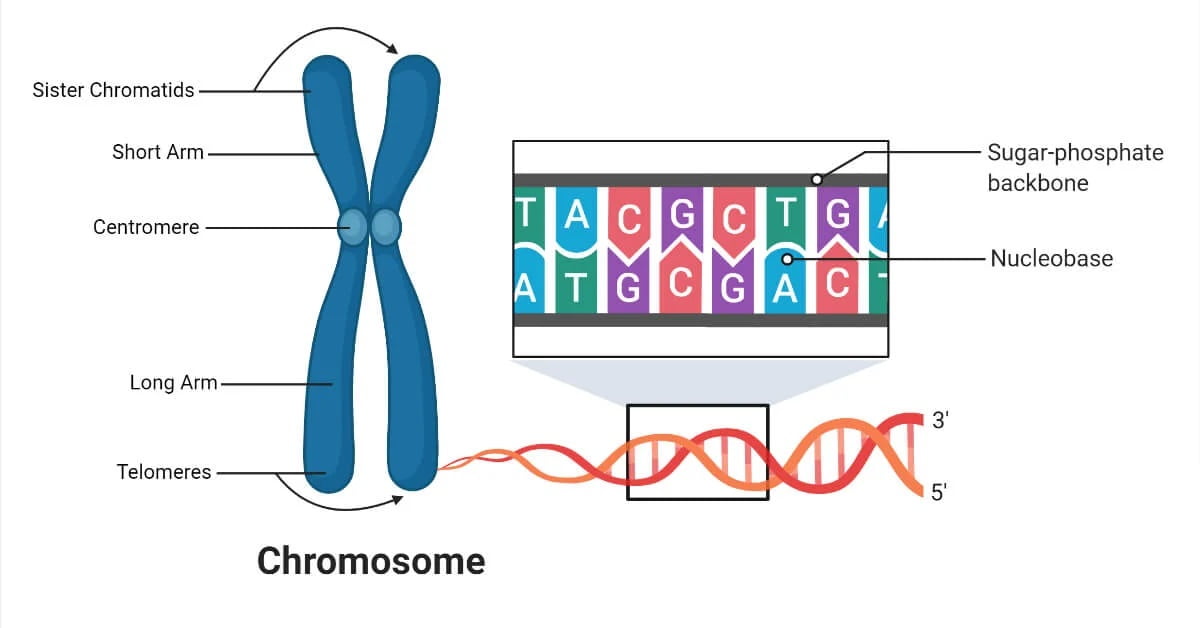
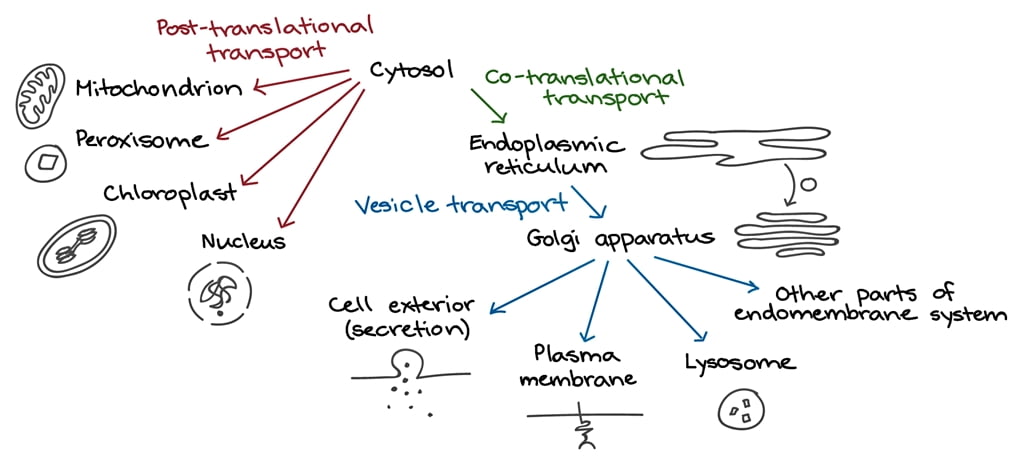
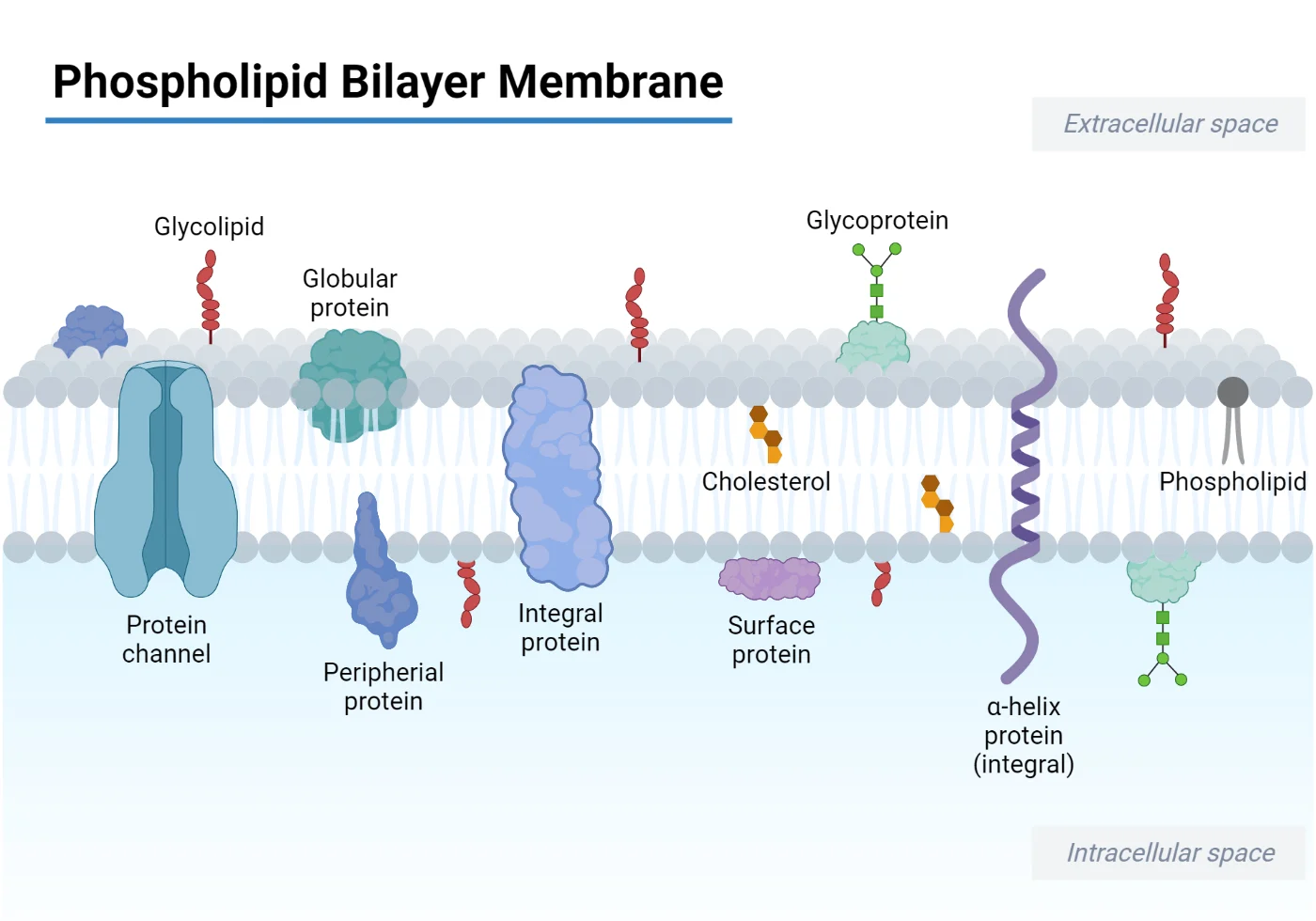
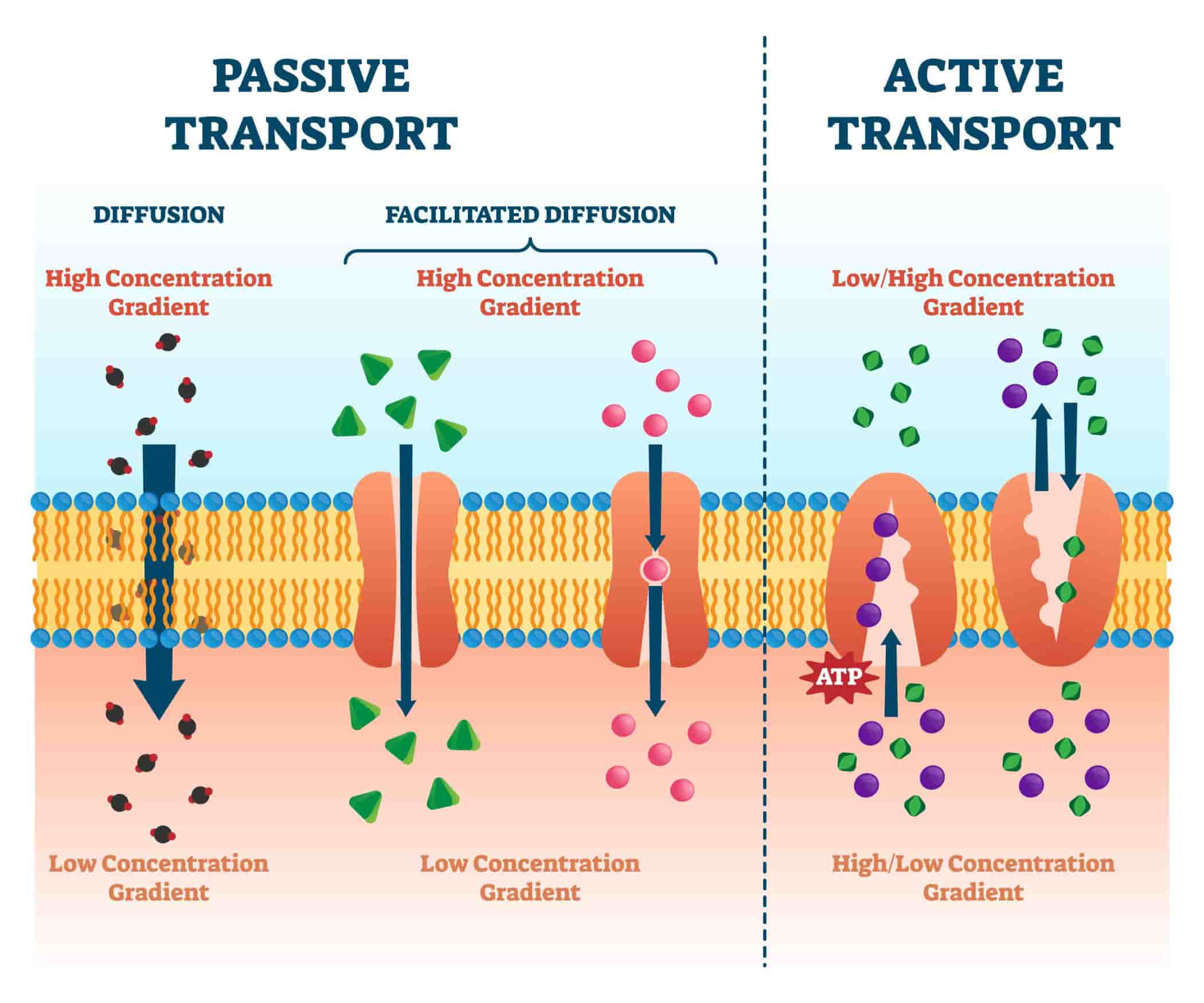
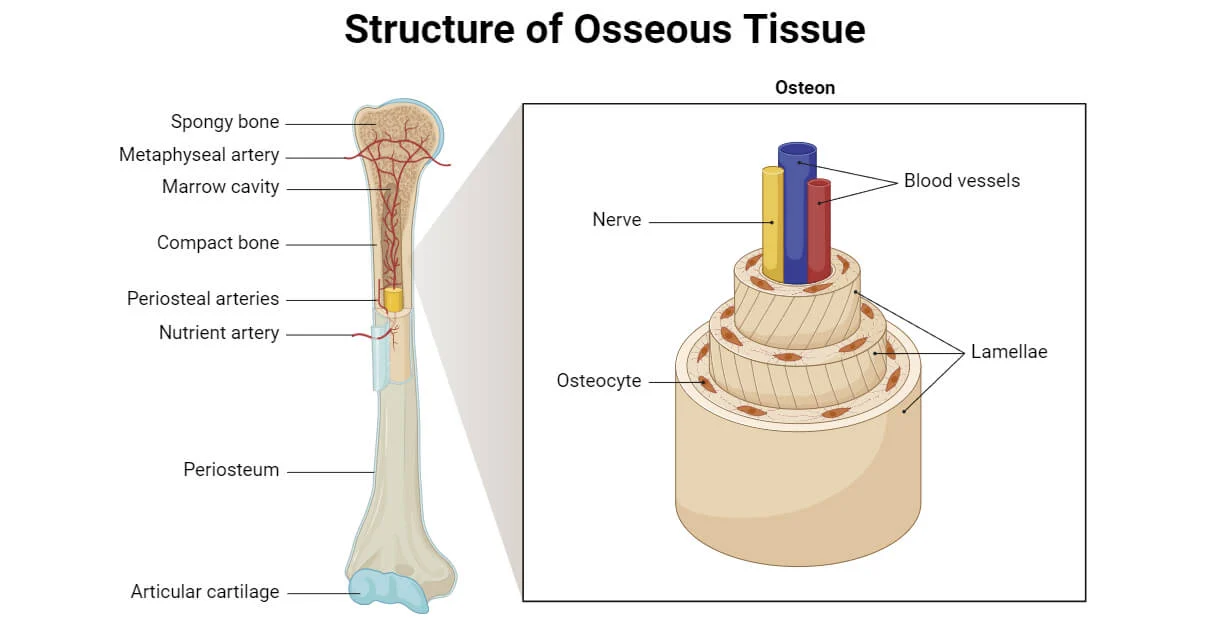
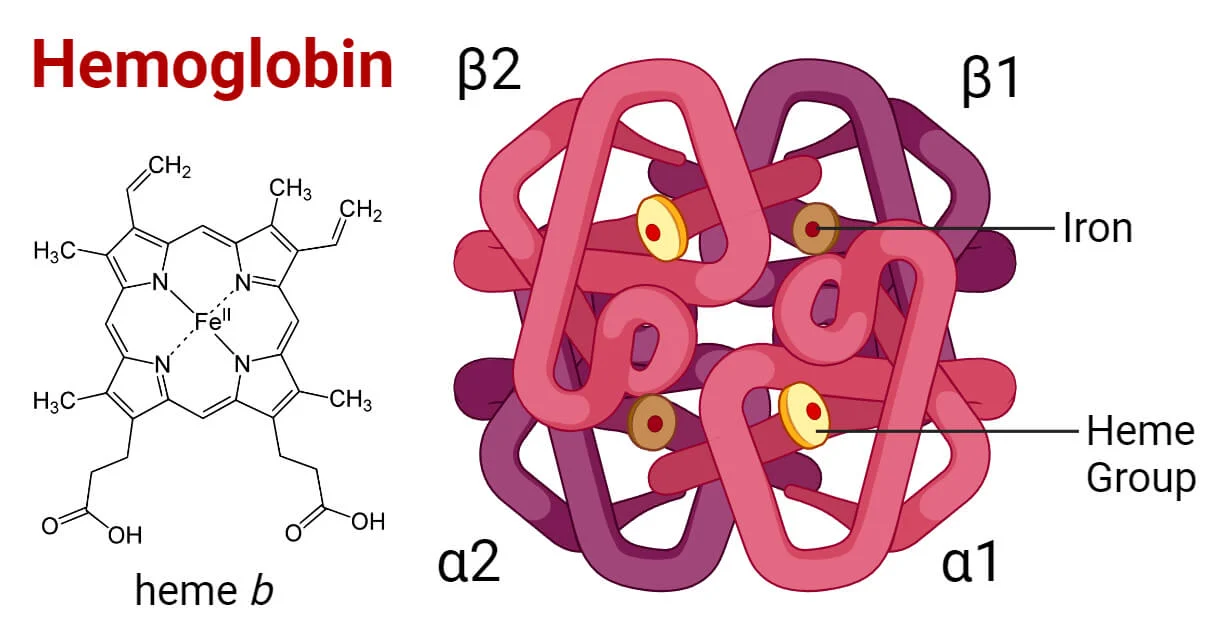
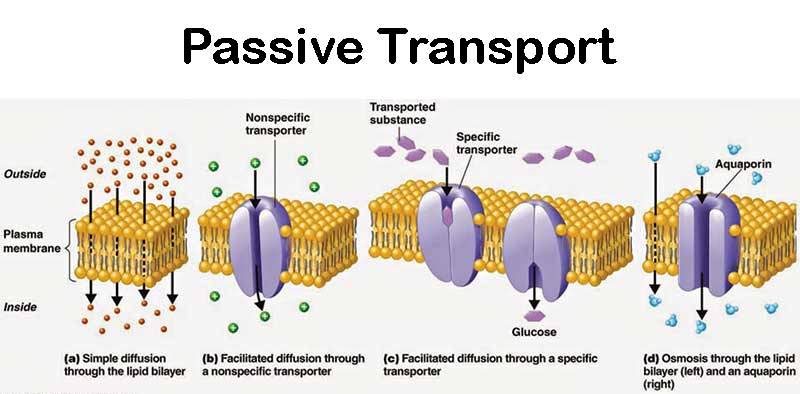
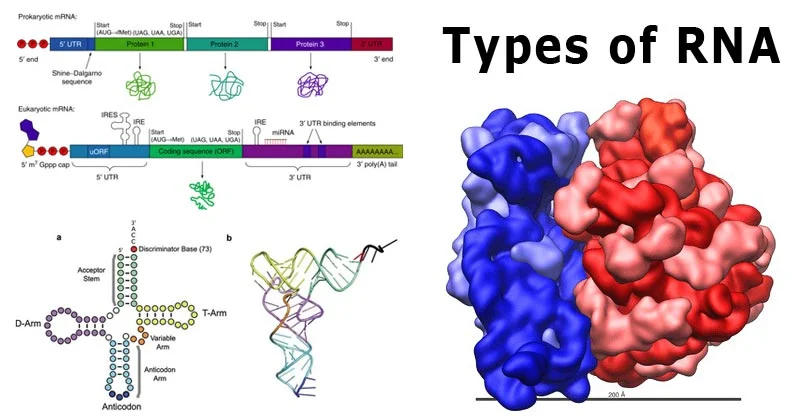
Cell Biology
Cell biology or cytology emerges as a vital branch of biology, delving into the intricate studies of cell structure and function. At its core, cell biology asserts that the cell stands as the fundamental unit of life. This branch serves as a gateway, providing a foundation for exploring tissues, organs, and the holistic understanding of the human body.
Cellular Diversity Across Organisms: The number of cells in an organism varies significantly, ranging from single-celled organisms to complex multicellular structures composed of billions of cells. For single-celled organisms, the focus lies on the singular cell, while multicellular organisms warrant a study of individual cells comprising various tissues.
Evolution of Cellular Studies: Initially, the study of cells was confined to external structures due to limitations in microscopic techniques. Advancements across scientific domains, however, have paved the way for probing the internal intricacies of cells. Beyond structure and function, cell biology extends its reach to explore cell communication, signaling, the cell cycle, and cell division, offering profound insights into an organism’s cellular composition.
Interdisciplinary Nexus: Cell biology intertwines with diverse disciplines such as genetics, molecular biology, cytochemistry, and biochemistry. Distinguishing cells into prokaryotic and eukaryotic categories based on complexity forms a fundamental aspect of this discipline.
Cellular Energetics and Metabolism: Intricacies of cellular metabolism and varied forms of cellular energy are explored through the lens of cell biology. By honing in on the structural and functional attributes of a single cell, researchers gain comprehensive insights into the broader complexities of the human body.
Advancements in Techniques: Technological progress has propelled cell biology forward, ushering in advanced imaging techniques that facilitate the observation of minute cellular organelles. This progress allows for efficient modification and observation of single cells, enhancing the depth of research in this field.
Interplay with Systemic Biology: Collaborating with systemic biology, cell biology tackles complex queries concerning cellular networks, evolutionary relationships between genomes, and the intricate biomolecular composition of diverse living organisms. Together, these branches unravel the tapestry of life’s blueprint.
Conclusion: Cell biology stands at the forefront of deciphering life’s blueprint, unraveling the mysteries locked within each cell. From fundamental units to complex organisms, cell biology serves as a cornerstone, weaving a narrative that connects the microscopic intricacies to the grand tapestry of life.