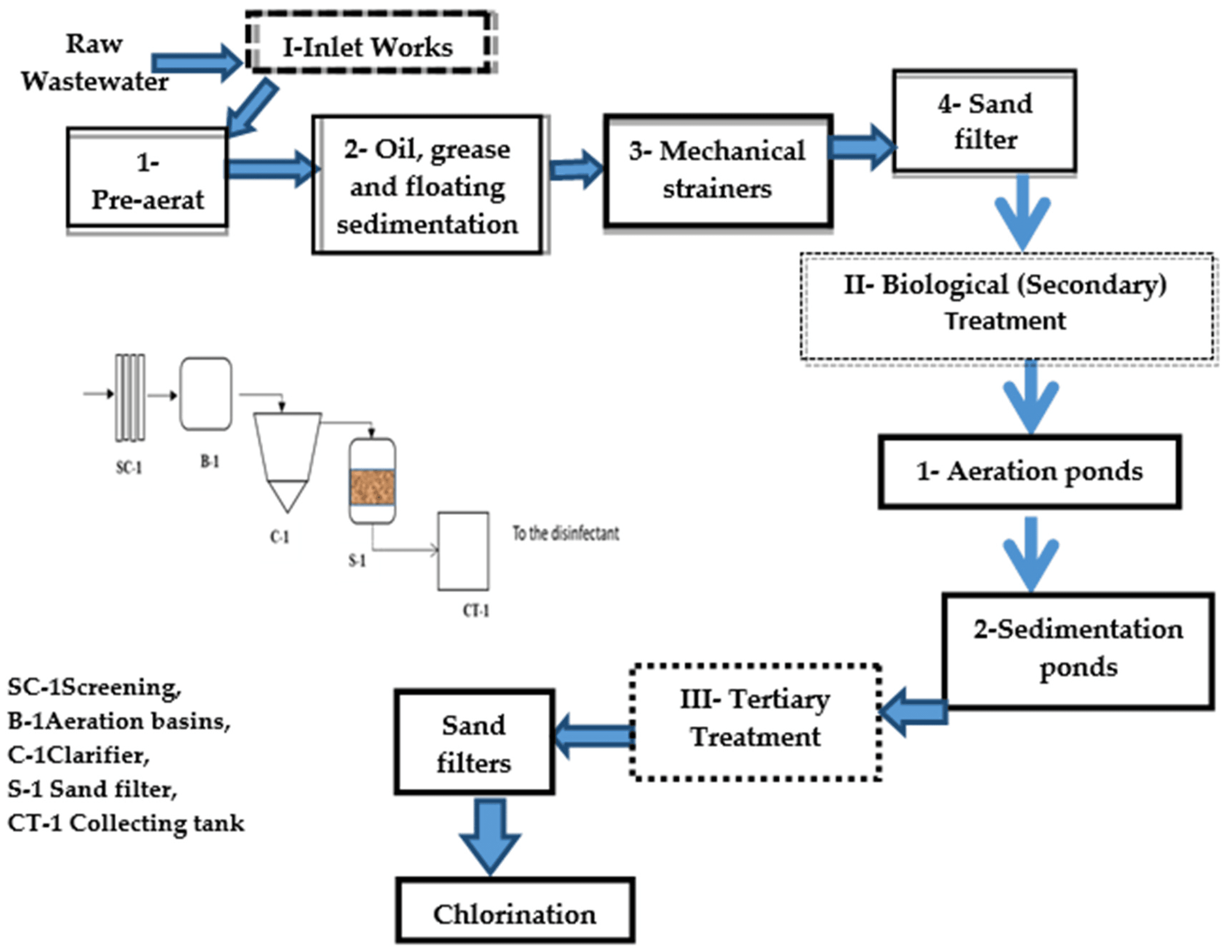
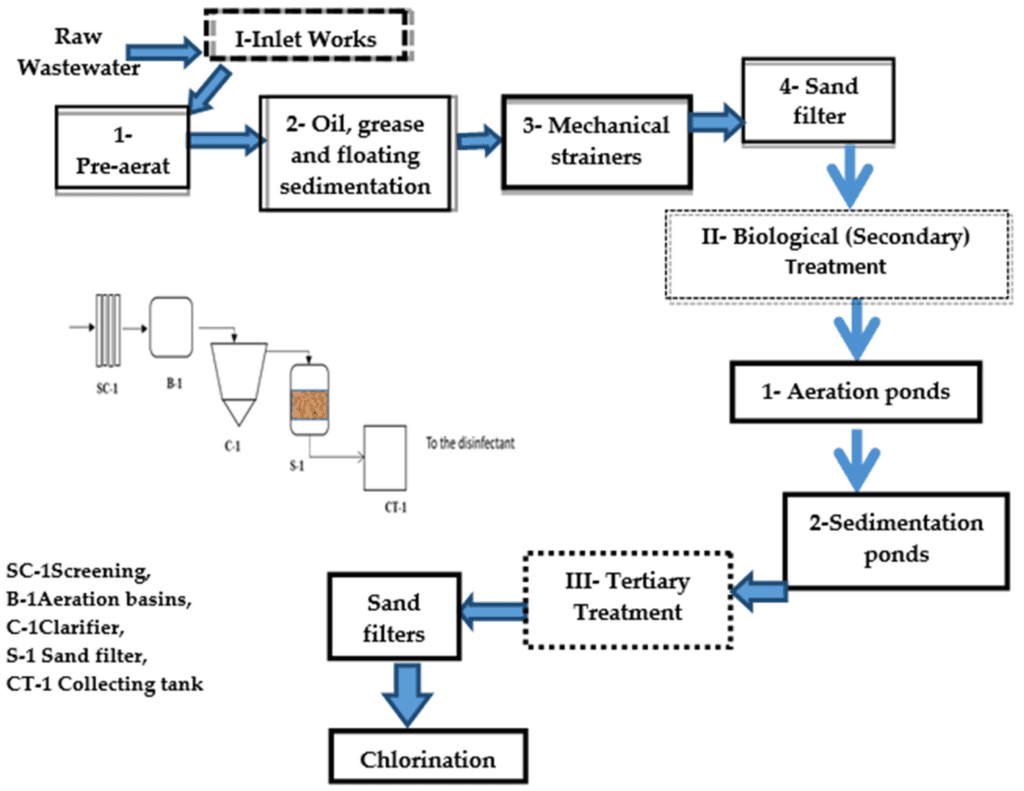
An oxidative ditch is an extended aeration system used in wastewater treatment. It is a modified activated sludge process designed for the biological treatment of municipal and industrial wastewater. The system is characterized by a continuous-loop channel, often constructed in a raceway or oval shape, where wastewater is aerated and mixed using mechanical aerators.
Key Features:
- Structure:
- The ditch is typically constructed from concrete or earthen materials, forming a loop or oval configuration.
- It allows for the continuous circulation of wastewater.
- Aeration:
- Mechanical aerators, or surface aerators, are used to introduce oxygen and mix the wastewater.
- Aeration supports the growth of microorganisms, which break down organic pollutants.
- Operation:
- Wastewater flows continuously through the ditch while microorganisms consume organic matter, ammonia, and nutrients.
- The treated effluent is clarified, and some sludge is recycled into the system to maintain the microbial population.
- Retention Time:
- Long hydraulic and sludge retention times enable effective treatment of wastewater.
Advantages:
- Efficient Treatment: Capable of removing organic matter, ammonia, and some nutrients.
- Simple Design: Easy to operate and maintain with relatively low energy requirements.
- Flexibility: Can handle fluctuations in wastewater flow and organic load.
- Odor Control: The aeration and mixing reduce odors compared to other treatment systems.
Limitations:
- Space Requirements: It requires a large area due to its extended aeration process.
- Energy Use: Continuous aeration demands a consistent power supply.
- Sludge Management: Proper handling and disposal of excess sludge are necessary.
Applications:
Oxidative ditches are commonly used in small- to medium-sized communities or industries where land is available and consistent treatment efficiency is required. Their simplicity and robustness make them a popular choice for decentralized wastewater treatment.