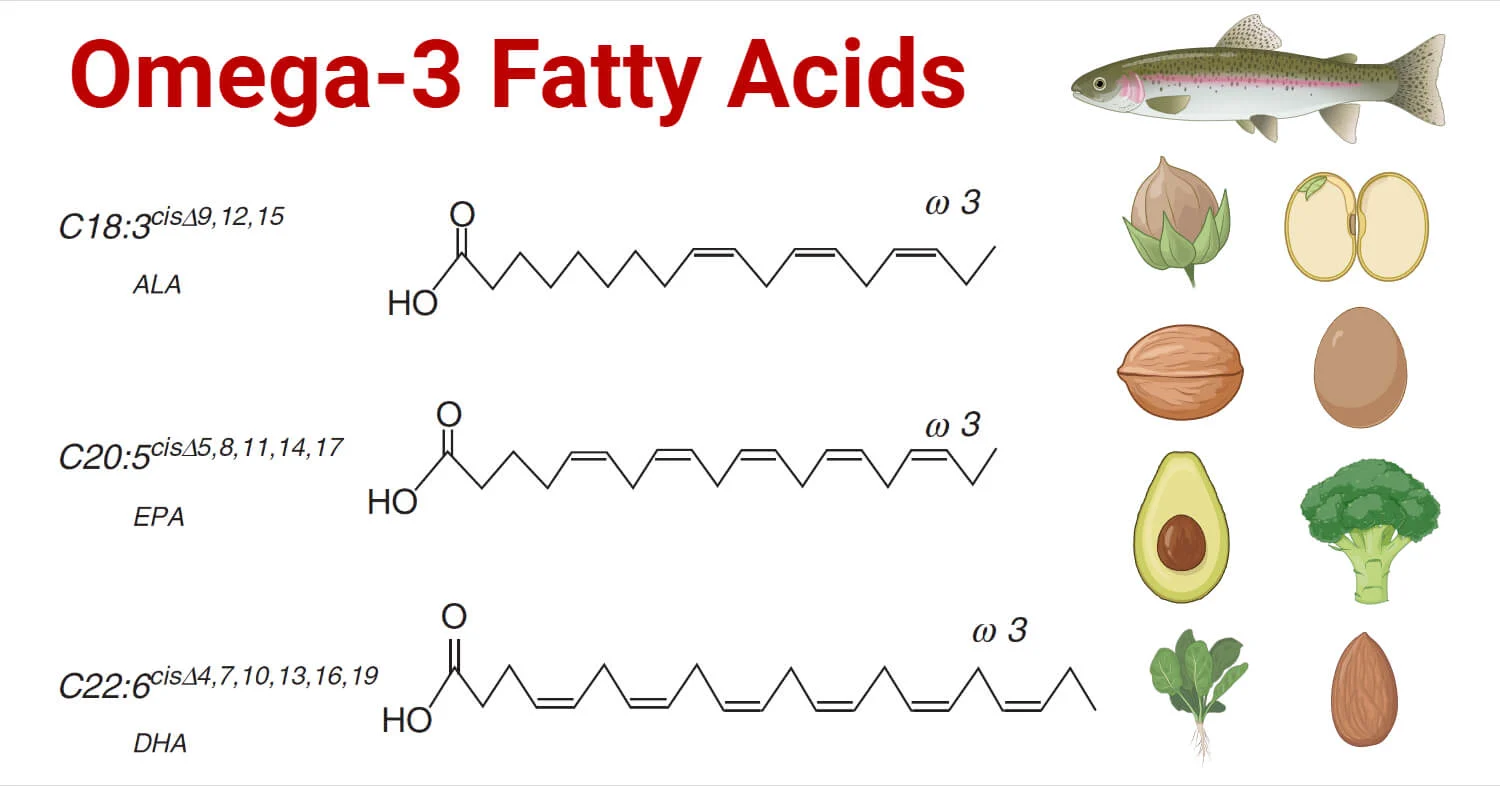
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is crucial for various bodily functions. These fats are essential because the body cannot produce them on its own, making them necessary to obtain from dietary sources or supplements. Omega-3 fatty acids have numerous health benefits, particularly for heart, brain, and eye health.
Functions of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids play various vital roles in the body:
- Muscle Function: Omega-3s are involved in muscle contraction and relaxation, helping to maintain proper muscle movement.
- Blood Clotting: They prevent excessive blood clotting by reducing platelet aggregation, thus lowering the risk of stroke and heart disease.
- Digestion: Omega-3s are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system by supporting the production of bile and aiding in the breakdown of fats.
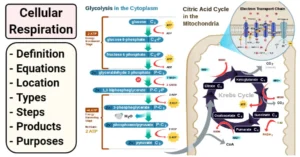
- Energy Production: Omega-3s are converted into energy in the body by transporting fatty acids into mitochondria.
- Cell Growth and Division: They play a crucial role in cell growth and division, helping in the repair and maintenance of tissues.
- Cell Membrane Formation: Omega-3s are key components of phospholipids, the molecules that form the cell membranes, influencing cellular communication and function.
- Anti-inflammatory Action: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, helping reduce inflammation in the body, which can prevent chronic diseases.
- Vision and Brain Health: DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid), a type of omega-3, supports healthy brain function and is important for the development of the retina in the eyes.
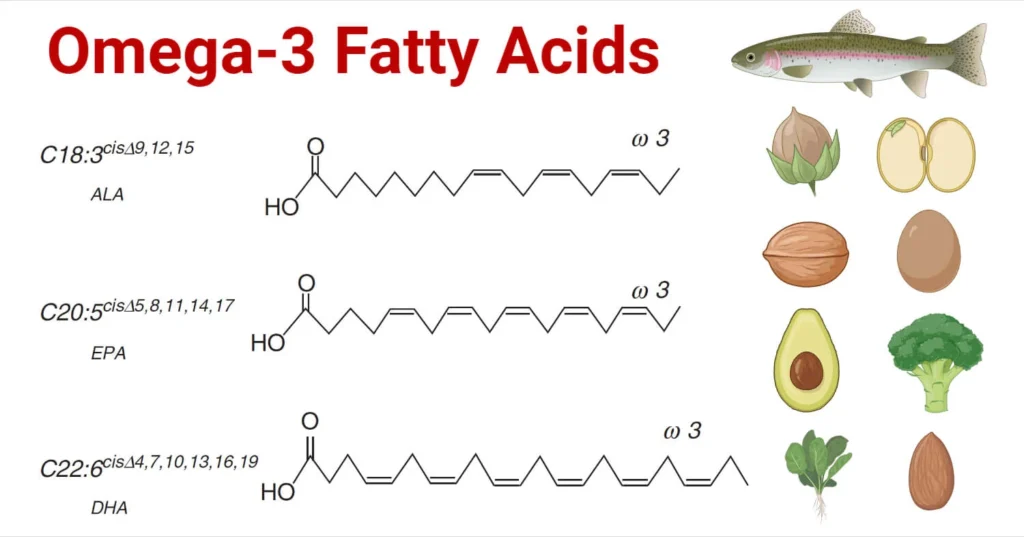
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in a variety of foods, particularly from marine and plant sources:
- Fatty Fish: Rich in long-chain omega-3s (EPA and DHA), common sources include:
- Salmon (wild-caught and farmed)
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Herring
- Tuna
- Trout
- Fish Oils: Supplements like fish oil, krill oil, and cod liver oil provide a concentrated source of omega-3s.
- Plant-based Sources:
- Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Hemp seeds
- Edamame
- Soybean oil
- Canola oil
- Avocados
- Spinach and broccoli
- Algal Oil: A plant-based source of DHA, especially beneficial for vegetarians and vegans.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are classified into three main types, each with different sources and benefits:
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA):
- Found primarily in fatty fish and fish oils.
- Plays a significant role in reducing inflammation, preventing heart disease, and improving mood.
- EPA helps produce eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules that reduce inflammation and support the immune system.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA):
- DHA is the most abundant omega-3 in the brain, retina, and sperm.
- Critical for brain function and development, particularly in the fetus during pregnancy.
- Found in high concentrations in fatty fish, fish oils, and algal oils.
- DHA helps improve cognitive function and supports the healthy functioning of the nervous system.
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA):
- A plant-based omega-3 found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and certain vegetable oils.
- ALA is converted into EPA and DHA in the body, although the conversion rate is low.
- ALA is primarily used by the body for energy production and cellular maintenance.
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids provide a wide range of health benefits, from cardiovascular protection to enhanced brain function:
- Heart Health:
- Omega-3s help lower the risk of heart disease by reducing triglycerides, lowering blood pressure, and decreasing the risk of arrhythmias.
- They can reduce blood clotting and decrease the plaque build-up in arteries.
- Mental Health:
- Omega-3s are known to help manage mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
- Studies suggest that omega-3s can improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and improve cognitive function.
- Brain Development:
- DHA is crucial for brain development in infants, particularly during pregnancy and early childhood.
- Omega-3s support learning, memory, and cognitive function, with DHA being particularly essential for maintaining brain health throughout life.
- Eye Health:
- DHA is a major component of the retina and helps maintain eye health.
- Omega-3s may reduce the risk of macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
- Reducing Inflammation:
- Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help treat conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis.
- They also help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Skin Health:
- Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the health and appearance of the skin by keeping it hydrated and reducing the risk of conditions like acne and eczema.
- Weight Management:
- Omega-3s may help control appetite, promote fat burning, and support weight management.
- Prevention of Chronic Diseases:
- Regular intake of omega-3 fatty acids may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, strokes, and certain cancers.
Symptoms of Omega-3 Deficiency
A lack of omega-3 fatty acids can lead to several health problems:
- Dry Skin: Omega-3s are important for skin hydration, and a deficiency can lead to dry, flaky skin.
- Joint Pain: A lack of omega-3s can result in increased inflammation and joint pain, especially in conditions like arthritis.
- Fatigue: Omega-3 deficiency may cause tiredness and low energy levels.
- Depression and Mood Disorders: Omega-3s play a crucial role in brain function, and a deficiency can contribute to symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
- Cognitive Decline: A lack of omega-3s can affect memory and cognitive function, potentially increasing the risk of dementia.
- Poor Heart Health: Omega-3s help reduce inflammation and improve cholesterol levels, so their absence can increase the risk of heart disease.
Side Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
While omega-3s are essential for good health, excessive consumption or supplementation may have side effects:
- Blood Thinning: High doses of omega-3s can increase the risk of bleeding and interact with blood-thinning medications like warfarin.
- Stomach Upset: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, when taking omega-3 supplements.
- Fishy Aftertaste: Fish oil supplements can cause a fishy aftertaste or burps in some individuals.
- Vitamin Toxicity: Overconsumption of fish oils can lead to an overdose of vitamins A and D, especially in cod liver oil, which may cause toxicity.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats with numerous health benefits, from improving heart health to supporting brain function and reducing inflammation. Ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3s through diet or supplements can contribute to overall well-being and help prevent various chronic health conditions. Incorporating sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts into your diet is a great way to ensure you’re getting enough omega-3s for optimal health.