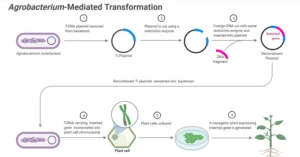
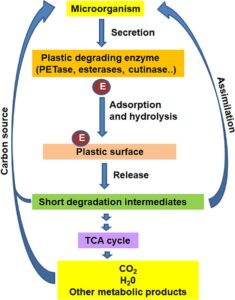
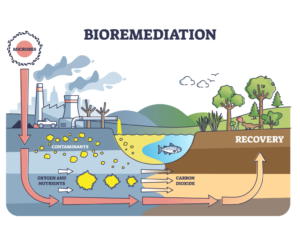
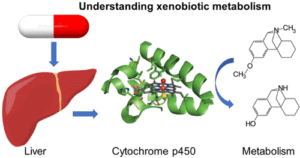
Nitrogen biofertilizers are natural fertilizers that contain nitrogen-fixing microorganisms capable of converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants. They play a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by enriching the soil with biologically available nitrogen, reducing the dependence on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, and enhancing soil fertility.
1. Importance of Nitrogen in Agriculture
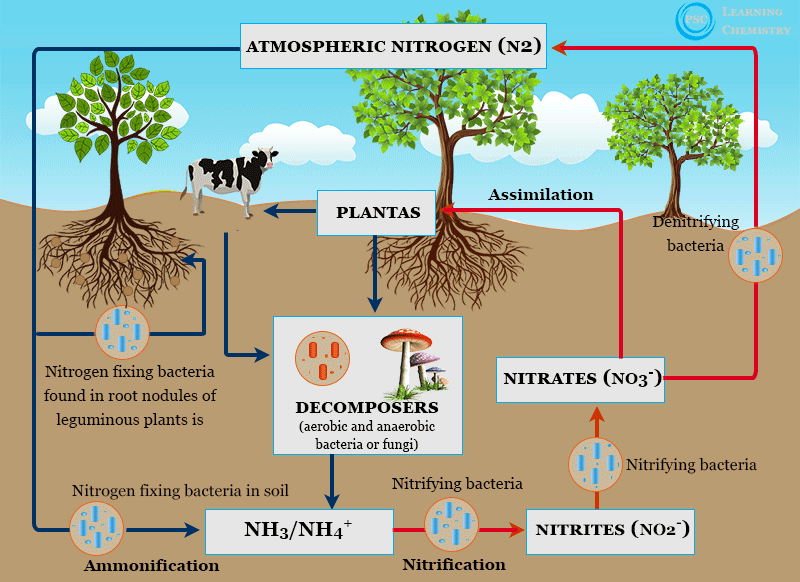
Nitrogen is a vital macronutrient required for plant growth and development. It is a key component of chlorophyll, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes. However, most plants cannot directly utilize atmospheric nitrogen (N2) and depend on its biologically fixed forms, such as ammonium (NH4–) and nitrate (NO3–).
2. Types of Nitrogen Biofertilizers
Nitrogen biofertilizers are classified based on the microorganisms they contain and their mode of action:
a. Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixers
- These microorganisms establish symbiotic relationships with specific host plants.
- Examples:
- Rhizobium spp.: Forms nodules on the roots of legumes (e.g., beans, peas, lentils) and fixes nitrogen.
- Frankia spp.: Associates with non-leguminous plants like Alnus and Casuarina to fix nitrogen.
- Cyanobacteria (Anabaena, Nostoc): Form symbiotic relationships with aquatic plants like Azolla in rice paddies.
b. Free-Living Nitrogen Fixers
- These bacteria and cyanobacteria fix nitrogen independently, without a plant host.
- Examples:
- Azotobacter spp.: Found in neutral to alkaline soils and fixes nitrogen aerobically.
- Beijerinckia spp.: Operates in acidic soils and enhances nitrogen availability.
- Cyanobacteria (Oscillatoria, Spirulina): Fix nitrogen in waterlogged soils.
c. Associative Nitrogen Fixers
- These microorganisms live in close association with plant roots but do not form nodules.
- Examples:
- Azospirillum spp.: Associates with cereals like wheat, maize, and rice, promoting nitrogen fixation and plant growth.
3. Mechanism of Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation involves the enzymatic conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2_22) into ammonia (NH3_33) using the nitrogenase enzyme complex. The process requires:
- High energy (ATP) derived from microbial metabolism.
- Reducing power in the form of electrons or hydrogen ions.
The ammonia produced is assimilated into organic compounds like glutamine and incorporated into plant tissues.
4. Benefits of Nitrogen Biofertilizers
- Eco-Friendly: Reduce environmental pollution caused by synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
- Cost-Effective: Lower input costs for farmers by reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Improves Soil Health: Enhance soil fertility and microbial diversity.
- Sustainable Productivity: Promote long-term agricultural productivity.
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Decrease nitrous oxide emissions associated with synthetic fertilizers.
5. Limitations of Nitrogen Biofertilizers
- Environmental Sensitivity: Efficacy depends on factors like temperature, moisture, and soil pH.
- Slower Action: Effects may take longer to become apparent compared to chemical fertilizers.
- Specificity: Some biofertilizers are effective only with specific crops or soil types.
- Storage Issues: Require proper storage conditions to maintain microbial viability.
6. Applications of Nitrogen Biofertilizers
- Legume Cultivation: Rhizobium-based biofertilizers are widely used in pulse crops.
- Cereal Crops: Associative and free-living nitrogen fixers like Azospirillum and Azotobacter enhance yields in rice, wheat, and maize.
- Aquatic Systems: Cyanobacteria like Anabaena in Azolla are used in rice paddies for nitrogen enrichment.
7. Examples of Nitrogen Biofertilizer Products
- Rhizobium-based inoculants for legumes.
- Azotobacter and Azospirillum formulations for cereals and vegetables.
- Azolla-cyanobacteria systems for wetland rice cultivation.
Nitrogen biofertilizers are essential tools for sustainable agriculture, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic fertilizers. Their use enhances nitrogen availability, improves soil health, and supports global efforts to promote eco-friendly farming practices. Increased adoption of nitrogen biofertilizers can contribute significantly to achieving food security while preserving environmental integrity.