Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that delves into the study of cellular molecules, particularly proteins and nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. These molecules are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cellular processes. Here are some key points about molecular biology:
- Focus on Nucleic Acids: The primary focus of molecular biology is on nucleic acids, especially DNA and RNA. This includes understanding their structure, composition, expression, and interactions within the cellular environment.
- Role in Cellular Functions: Molecular biology has gained significance by revealing the critical roles nucleic acids and other biomolecules play in the normal functioning of living organisms. This knowledge has broad implications for various fields, including medicine and biotechnology.
- Emergence as a Distinct Discipline: Molecular biology emerged as a separate discipline from related fields like biochemistry, genetics, and biophysics. It has its own set of principles, methods, and techniques for studying cellular molecules.
- Techniques and Methods: Various techniques have been developed in molecular biology, with some borrowed from genetics. Common methods include X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy for determining the three-dimensional structure of nucleic acids.
- Genetic Engineering: Molecular biology focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms of genetic processes. This knowledge is crucial for genetic engineering, allowing scientists to isolate, modify, and sequence genes for various applications.
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Studies: Initial studies were often based on the genetics of simple bacteria like E. coli. However, many principles and techniques developed for prokaryotes have been successfully applied to eukaryotic cells.
- Advances in DNA Technology: Modern advancements in recombinant DNA technology have made ambitious projects possible, such as sequencing the complete genome of organisms, including humans, using techniques like DNA sequencing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- Clinical Applications: Molecular biology has found applications in clinical research and medical therapies, particularly in gene therapy. Understanding molecular mechanisms allows for targeted drug development and efficient disease diagnosis.
Molecular biology continues to be a dynamic and evolving field, contributing significantly to our understanding of life at the molecular level and offering practical applications across various scientific disciplines.
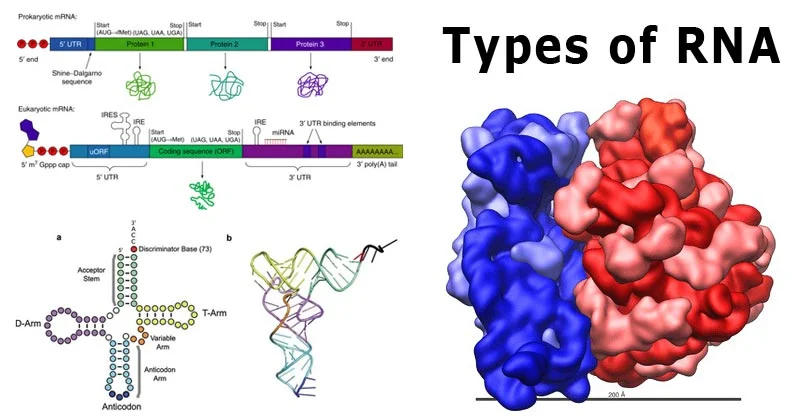
7 Types of RNA with Structure and Functions
What is RNA? Its full form is Ribonucleic acid. This is a polymer of subunits joined by phosphodiester bonds. It is a single-stranded nucleic acid similar to DNA but having ribose sugar rather than ... Read more
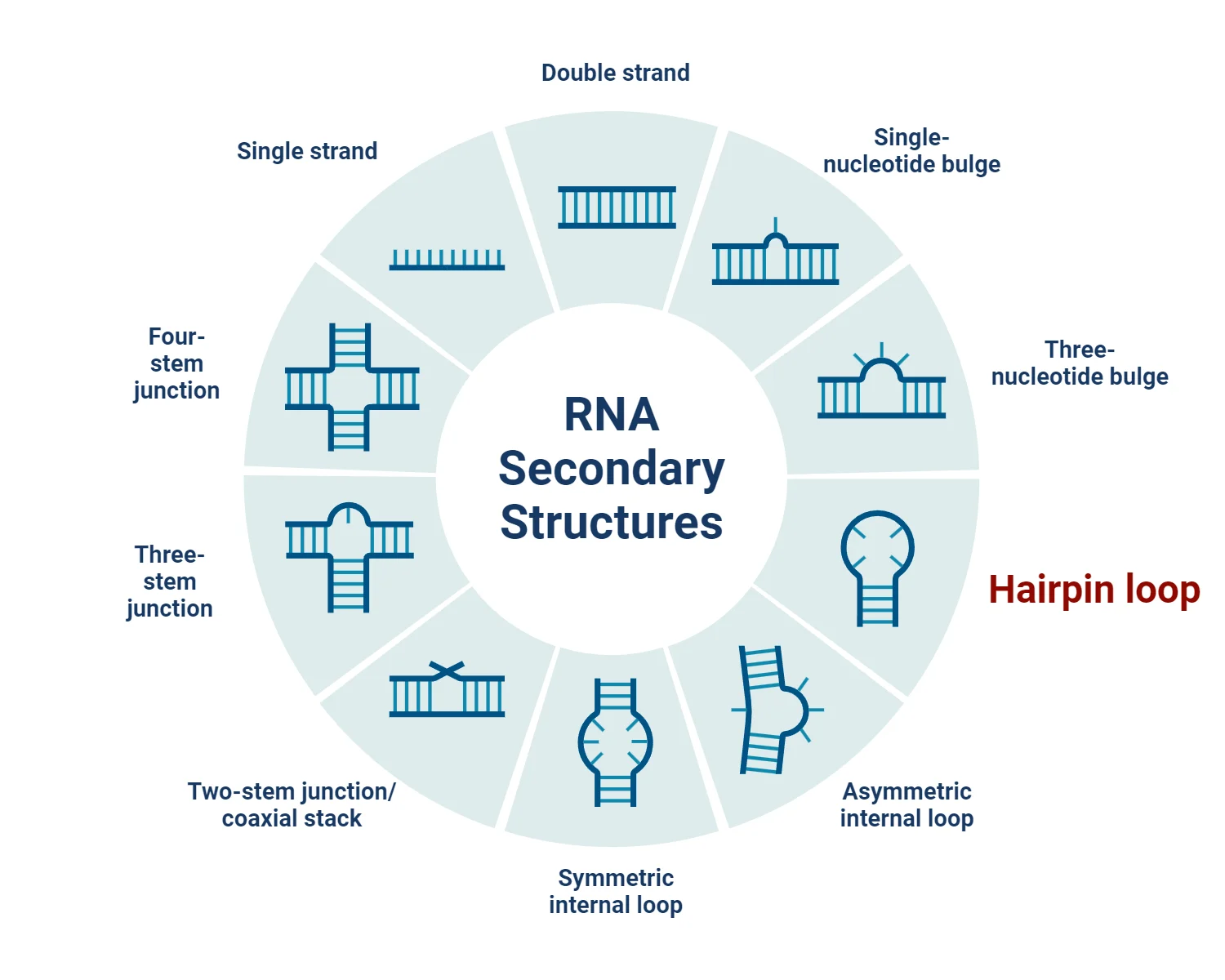
Stem-loop (Hairpin Loop): Properties, Types, Examples, Uses
Stem-loop, also known as a hairpin loop, is a common secondary structure found in nucleic acids, particularly in single-stranded RNA and DNA molecules. This structure plays a critical role in various biological processes ... Read more
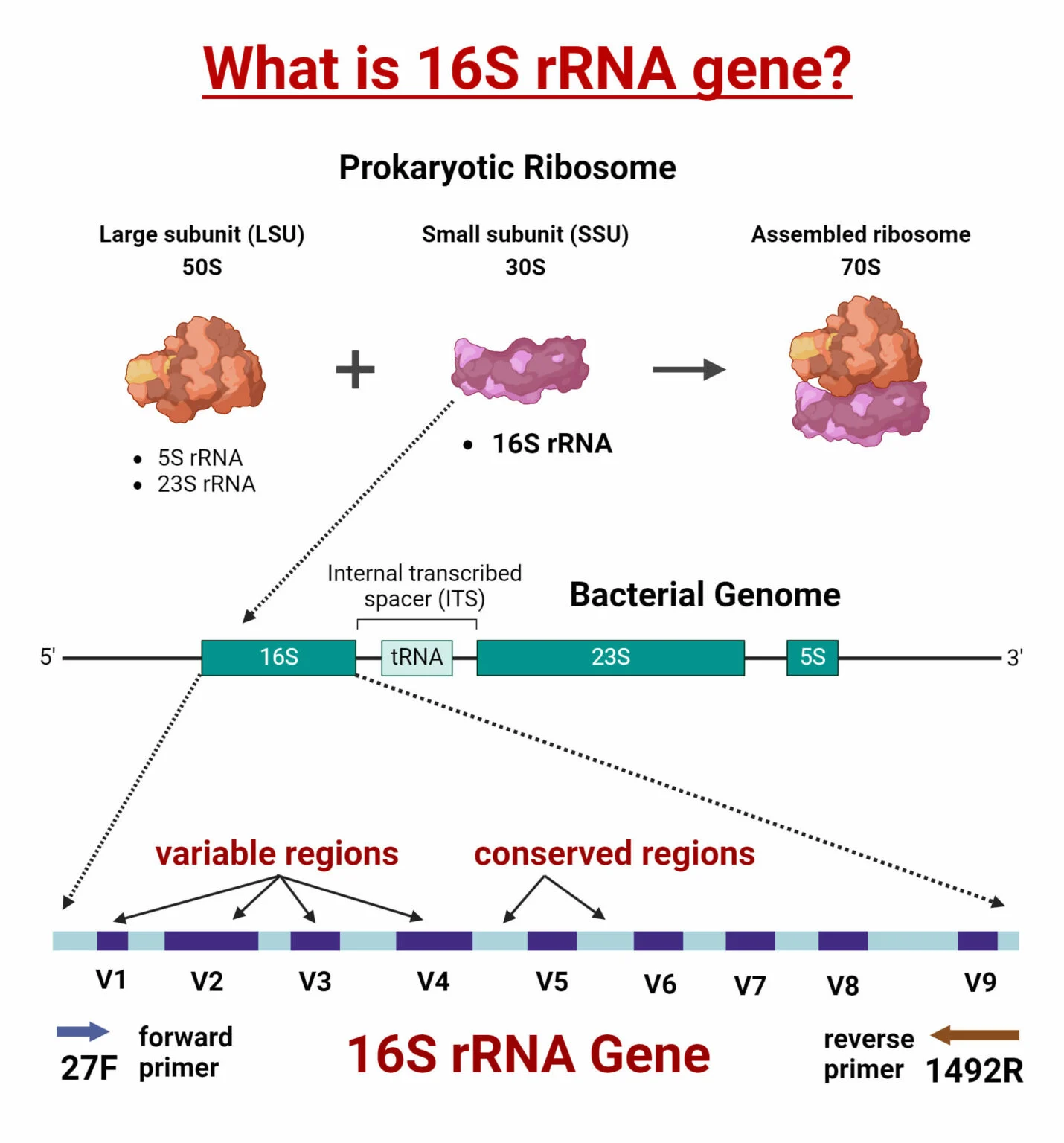
16S rRNA Gene Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Uses, and Applications
What is the 16S rRNA Gene? The 16S rRNA gene is a widely used genetic marker for bacterial taxonomy and phylogeny. Found in the ribosomes of prokaryotes, the 16S rRNA gene is about ... Read more
Illumina Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Uses, and Diagram
Illumina sequencing, often referred to as next-generation sequencing (NGS), is one of the most widely adopted methods for high-throughput DNA sequencing. It leverages sequencing by synthesis (SBS) technology to detect individual DNA bases ... Read more
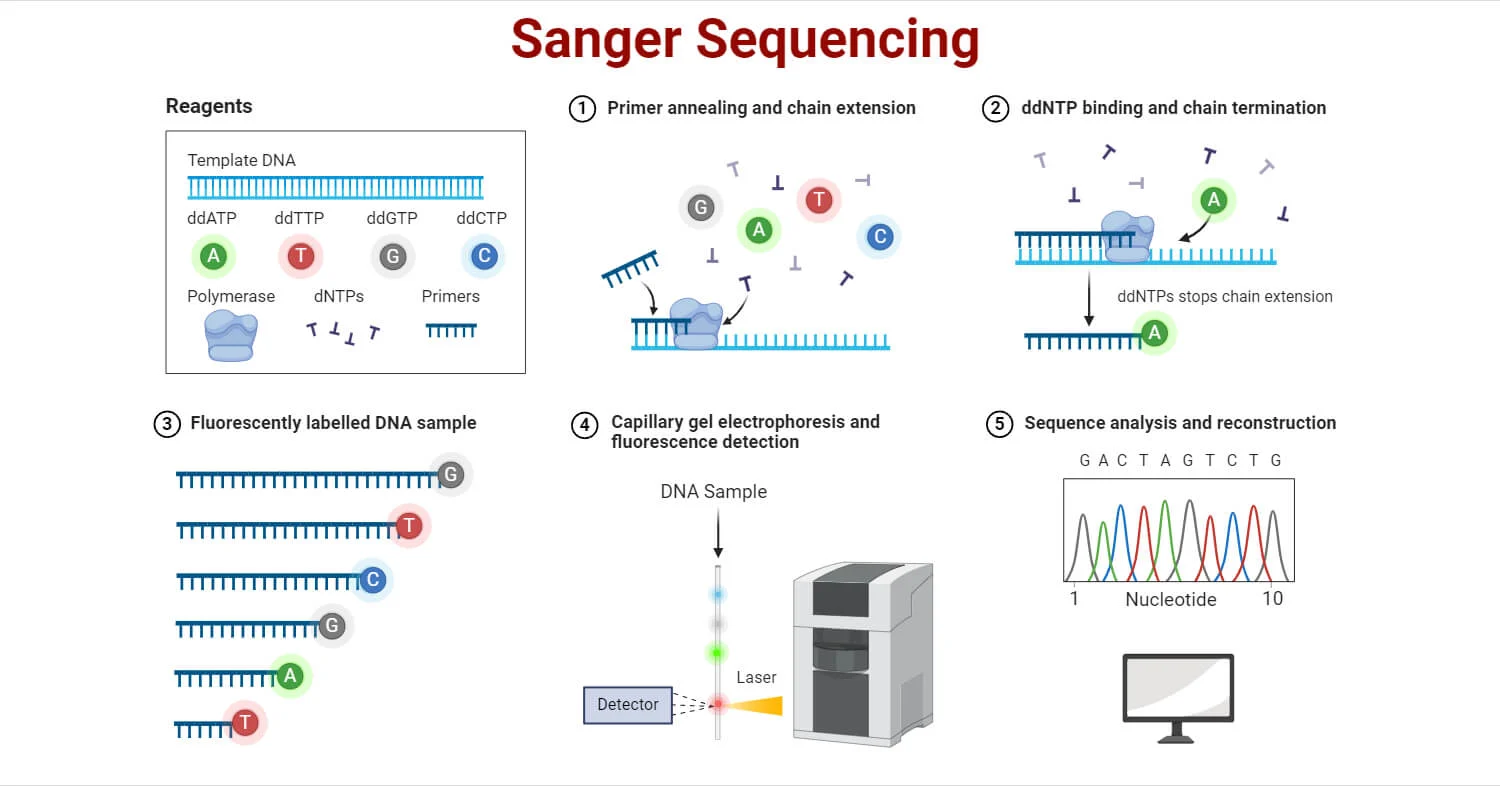
Sanger Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Applications, Diagram
Principle of Sanger Sequencing: Sanger sequencing, also known as dideoxy sequencing or chain termination method, identifies the nucleotide sequence of DNA by incorporating modified nucleotides called dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs). These ddNTPs lack the ... Read more
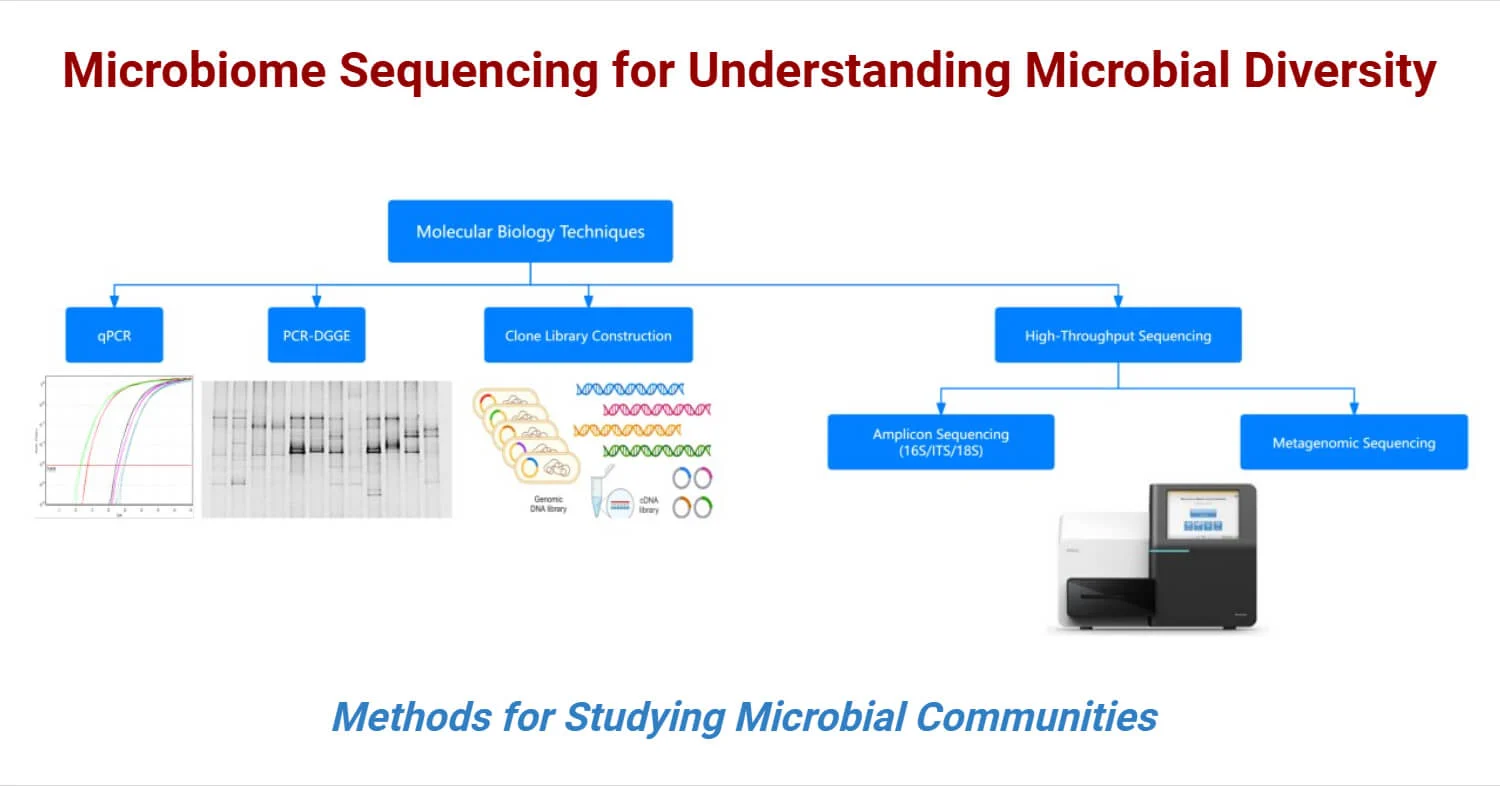
Microbiome Sequencing for Understanding Microbial Diversity
Microbiome sequencing is a pivotal technique for analyzing the diverse communities of microorganisms—such as bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses—that inhabit various environments, including the human body. This process enables researchers to explore the ... Read more
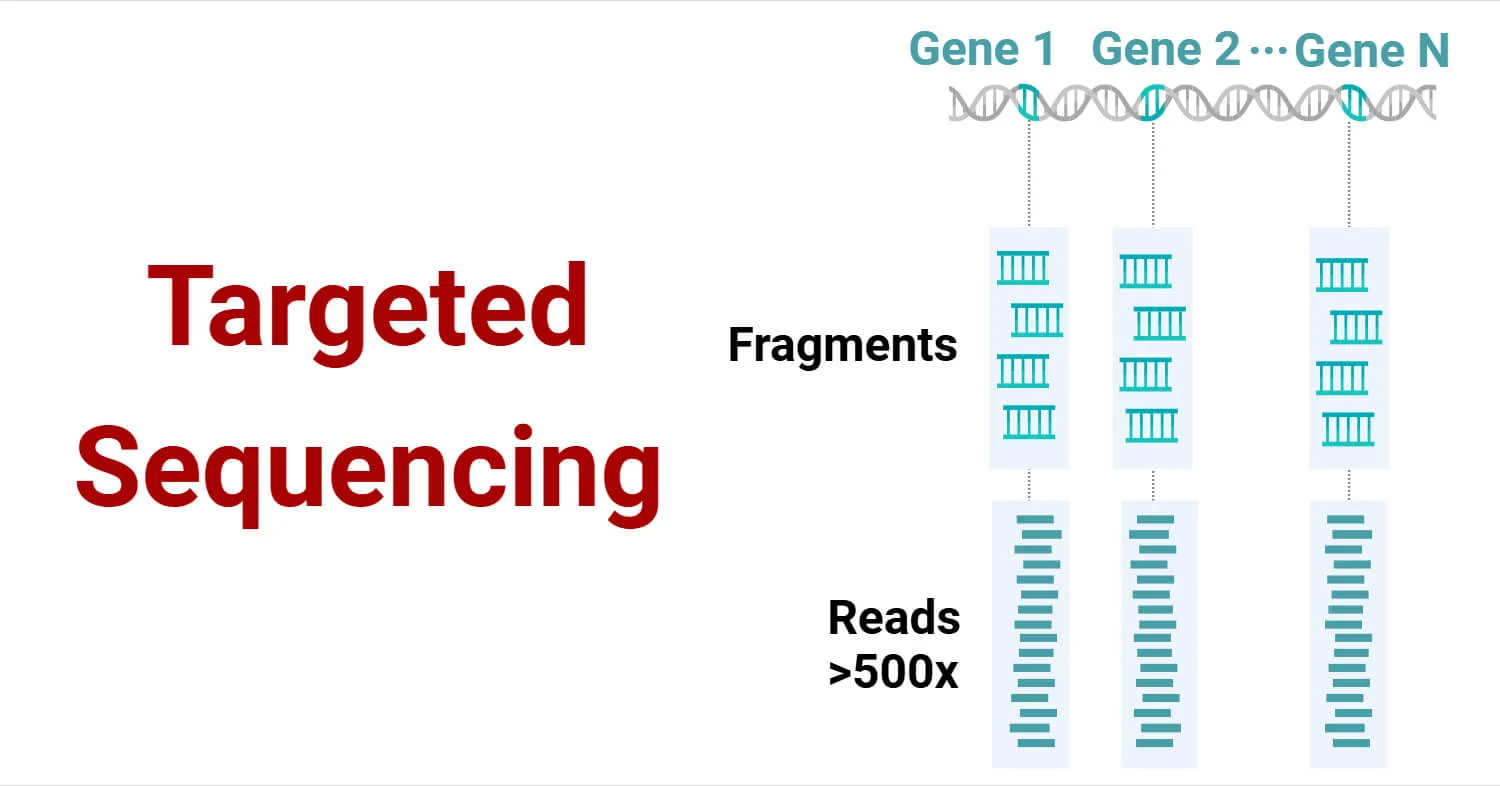
Targeted Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Methods, Uses, Diagram
Targeted sequencing is a method of sequencing specific genomic regions of interest rather than sequencing the entire genome. This approach is highly effective for analyzing particular genes or regions, offering a more efficient ... Read more
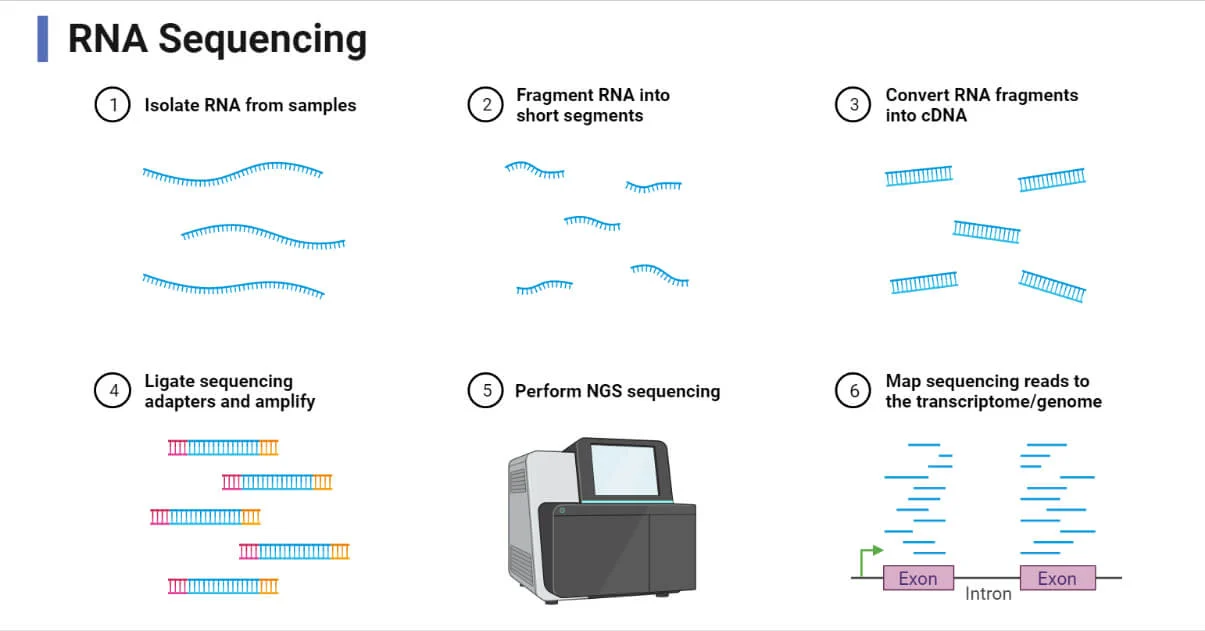
RNA Sequencing: Definition, Principle, Steps, Types, and Applications
RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) is a revolutionary molecular biology technique that allows for the comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome, providing insights into the gene expression levels of a cell. This technology has transformed transcriptomics, ... Read more
Helicos Single-Molecule Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Uses
Helicos Single-Molecule Sequencing (tSMS) is a third-generation DNA sequencing technology that directly sequences individual DNA or RNA molecules without requiring amplification. Launched in 2008 by Helicos Biosciences, it revolutionized sequencing by minimizing preparation ... Read more
Exploring the Potential of CRISPR-Cas9: Revolutionizing Genetic Engineering
CRISPR : Imagine having a tool that could rewrite the blueprint of life with incredible precision. That’s exactly what CRISPR-Cas9 is—a revolutionary discovery that has opened up new frontiers in genetic engineering. Originally ... Read more