Genetics
Genetics is a scientific branch focused on heredity, encompassing gene transmission, regulation, and manipulation.
Interdisciplinary Connection:
Serves as a crucial link connecting various disciplines, including microbiology, biotechnology, medicine, and agriculture.
Historical Development:
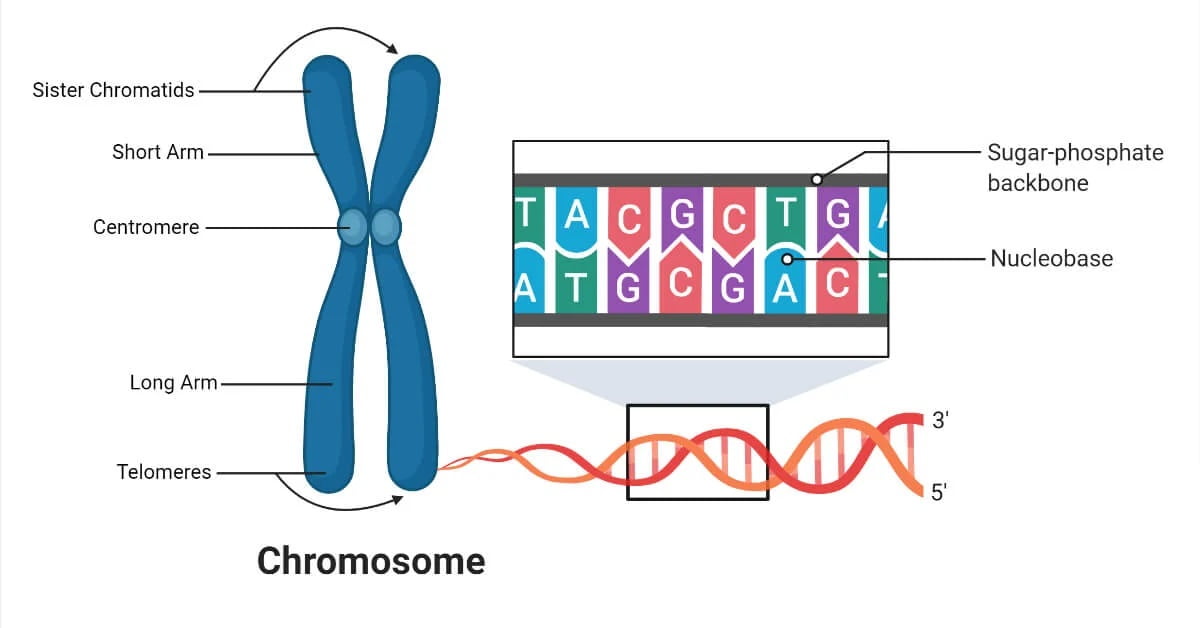
Studies on genes and chromosomes commenced relatively late, requiring advancements in microscopy.
Recognition of heredity’s impact on cultivation and organism production dates back to ancient times.
Mendel’s Contributions:
Genetics gained prominence with Mendel’s pea plant studies, further developed by the influential work of Morgan.
Evolution into a Distinct Field:
Emerged as a distinct field with gene identification and comprehensive studies on gene roles, regulation, and expression.
Historical Techniques vs. Modern Advances:
Initial understanding relied on techniques like Punnet’s square.
Modern genetics evolved with advancements such as X-ray diffraction, revealing DNA structure and genetic code presence.
Focus of Modern Genetics:
Modern genetics centers on the chemical composition of genetic structures, particularly DNA, influencing cellular chemical reactions.
Factors Influencing Gene Expression:
Gene expression is influenced by genetic composition and environmental factors.
Environmental Influence:
Environmental impact on gene expression is evident in green plants, where chlorophyll formation genes are expressed only in sunlight.
Genetic Influence on Health:
Genes, via encoded proteins, determine metabolism efficiency, detoxification of toxins, and immune response strength.
Mutation and Genetic Diseases:
Mutations, influenced by genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors, contribute significantly to major genetic diseases.