Biochemistry
Biochemistry, a profound branch of science, delves into the intricate tapestry of life at the molecular level. It revolves around the study of biomolecules, deciphering their structure, composition, and metabolism within diverse living organisms. Often referred to as ‘biological chemistry,’ biochemistry amalgamates techniques from analytical, inorganic, and organic chemistry to elucidate the chemistry of life.
Metabolic Dynamics:
The metabolic processes in living beings encompass catabolic and anabolic processes, involving intricate biochemical compounds. These processes orchestrate the breakdown and synthesis of biomolecules crucial for life.
Understanding Biomolecules:
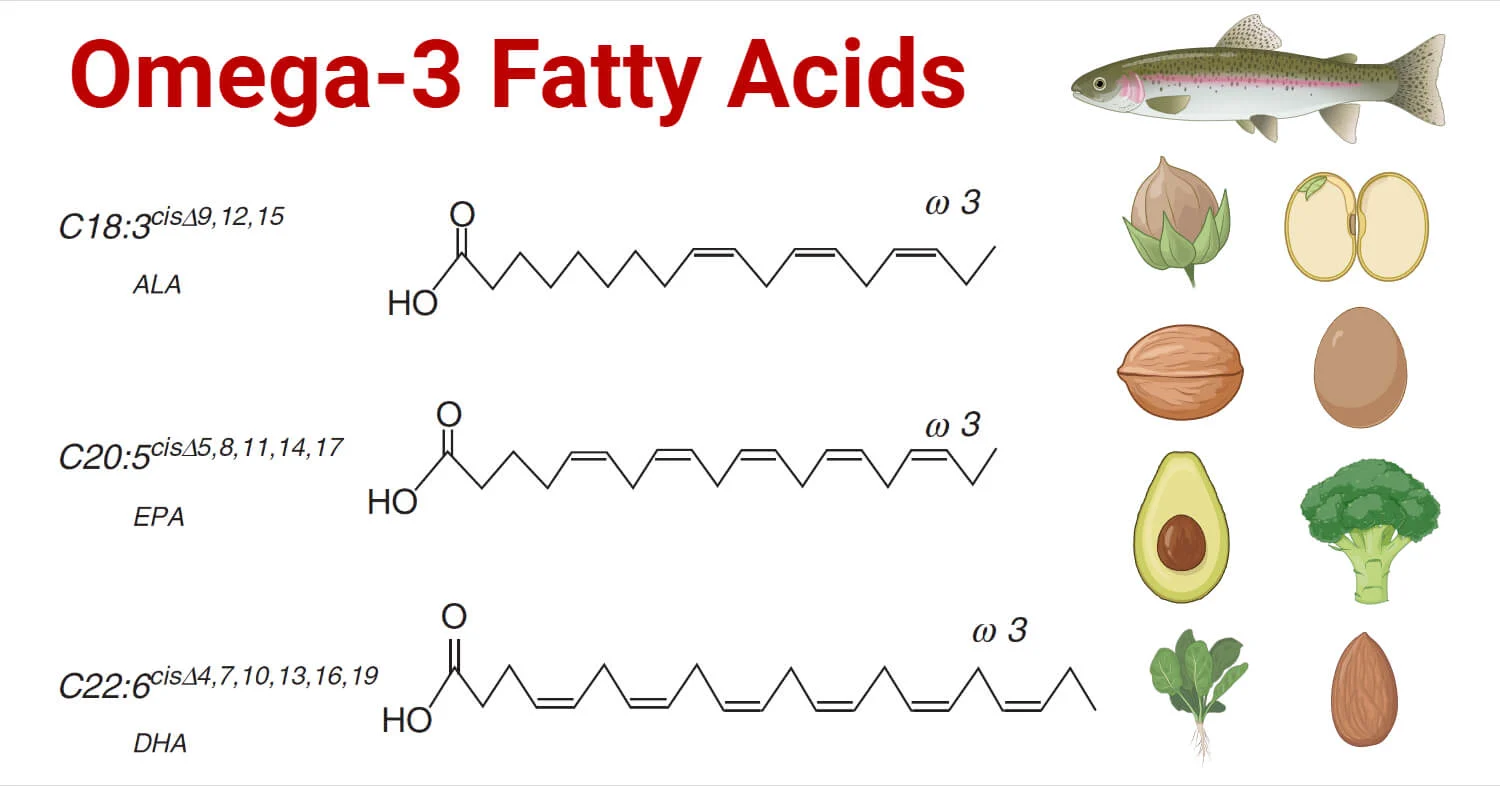
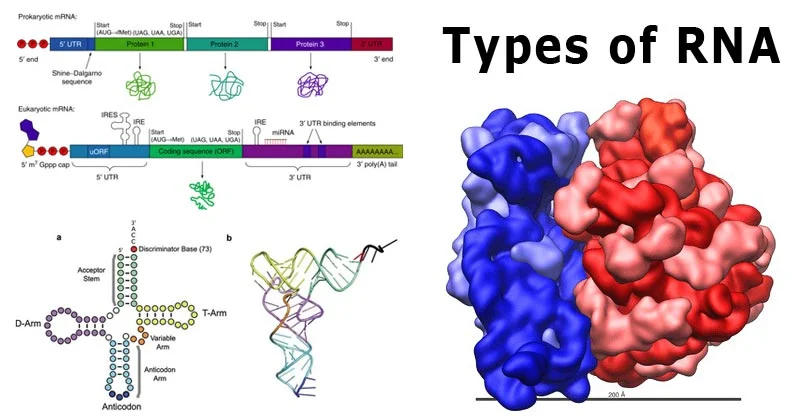
Vital biomolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids, and vitamins serve as integral structural and physiological components of living organisms. The study of their biochemical composition is pivotal, unraveling the molecular mechanisms behind phenomena like respiration, photosynthesis, and fermentation.
Applications and Impacts:
The insights gained from biochemistry have far-reaching applications in industries, nutrition, medicine, and agriculture. Biochemical reactions, enzyme activities, and substrate/product concentrations provide crucial information about organisms, shaping various fields.
Biochemical Testing:
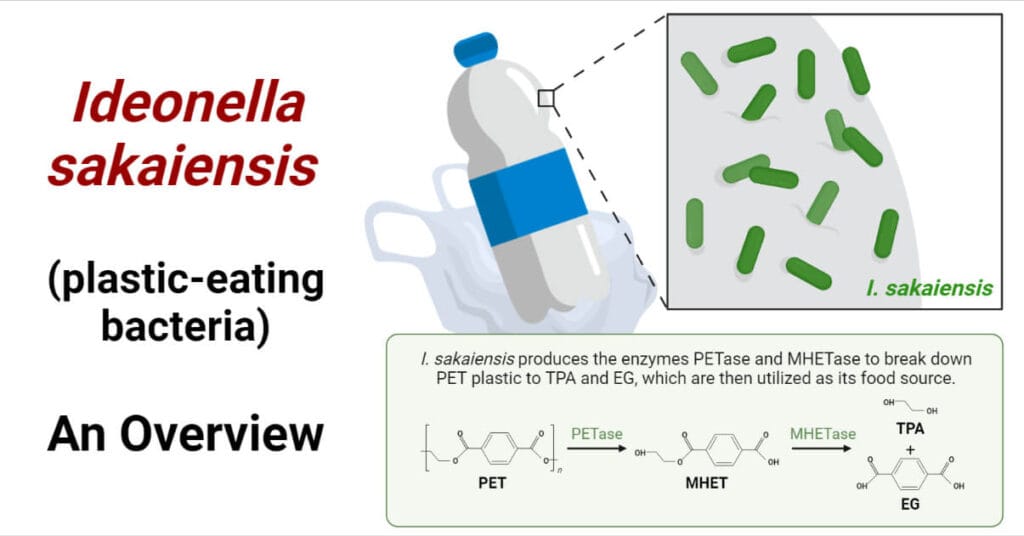
Biochemical reactions serve as the foundation for biochemical testing, aiding in the identification and differentiation of microorganisms. Results from these tests find applications in the production of pharmaceuticals targeting specific metabolic processes.
Interdisciplinary Integration:
Biochemical techniques seamlessly integrate with diverse fields such as agriculture, genetics, molecular biology, and biophysics. This interdisciplinary approach enhances the depth and scope of biochemistry, fostering innovation and discovery.
Clinical Significance:
Biochemistry contributes significantly to the understanding of nutritional requirements for different organisms. Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis of diseases, with biochemical compounds utilized in identifying conditions like diabetes.
Genetic Insights:
Determination of the genetic composition, a facet of biochemistry, aids in genetic studies and the diagnosis of genetic diseases. This facet provides a profound understanding of the genetic underpinnings of life.
Evolutionary Perspective:
Biochemical analysis of biomolecules contributes to studies on the origin and evolution of living beings. Unraveling the molecular intricacies sheds light on the complex relationships between different groups of organisms.
Conclusion:
In essence, biochemistry serves as a key to unravel the mysteries of life, providing a comprehensive understanding of the molecular intricacies governing living organisms. From fundamental metabolic processes to applications in various industries and clinical settings, biochemistry stands as a cornerstone in scientific exploration, fostering advancements that echo across diverse scientific domains.