Biopesticides are natural pest control agents derived from biological sources such as microorganisms, plants, and certain minerals. They are used to manage pests in an environmentally sustainable manner, reducing the reliance on synthetic chemical pesticides that may have harmful effects on human health and the environment.

Types of Biopesticides
- Microbial Biopesticides:
- Derived from bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa.
- Examples:
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): Produces toxins that are lethal to specific insect larvae.
- Trichoderma spp.: Fungi used to control soil-borne fungal diseases.
- Beauveria bassiana: A fungus that infects and kills insects.
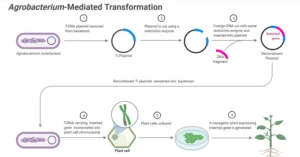
- Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs):
- Genetic material from biopesticidal organisms (e.g., Bt genes) is incorporated into crop plants through genetic engineering.
- Crops like Bt cotton and Bt corn produce their own insecticidal proteins.
- Biochemical Biopesticides:
- Naturally occurring substances like pheromones, plant extracts, and hormones that disrupt pest behavior.
- Examples:
- Neem-based products (e.g., azadirachtin) repel insects or inhibit their growth.
- Pheromone traps lure pests to reduce their populations.
- Mineral-Based Biopesticides:
- Include natural minerals such as sulfur and diatomaceous earth, which deter or kill pests.
Advantages of Biopesticides
- Environmental Safety:
- Biopesticides are biodegradable and leave minimal residues in the environment.
- Target Specificity:
- Most biopesticides affect only specific pests, reducing the impact on beneficial organisms like pollinators.
- Reduced Resistance Development:
- Pests are less likely to develop resistance due to diverse modes of action.
- Human Health Safety:
- Lower toxicity compared to synthetic chemicals, making them safer for applicators and consumers.
- Support for Organic Farming:
- Widely accepted in organic agriculture as sustainable pest management solutions.
Limitations of Biopesticides
- Slow Action:
- Often take longer to show effects compared to synthetic pesticides.
- Environmental Sensitivity:
- Effectiveness can be influenced by environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and UV light.
- Short Shelf Life:
- Many biopesticides have limited storage stability.
- Cost and Availability:
- Higher production costs and limited availability in some regions can hinder widespread adoption.
Applications of Biopesticides
- Agriculture: Managing insect pests, fungal pathogens, and weeds in crop production.
- Horticulture: Protecting fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
- Forestry: Controlling pests that threaten forest health.
- Public Health: Reducing vectors like mosquitoes to prevent disease spread.
Biopesticides are an essential component of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. Their use promotes sustainable agriculture, minimizes environmental pollution, and aligns with global efforts to reduce the ecological footprint of farming practices. Continuous research and innovation in biopesticide development will enhance their effectiveness and affordability, driving their adoption worldwide.