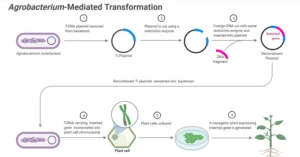
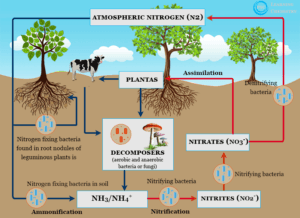
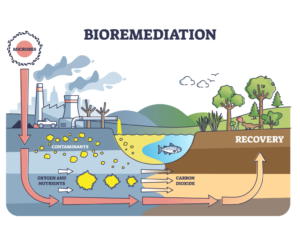
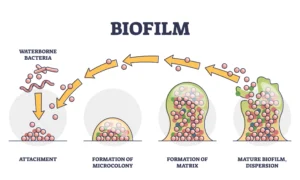
Biofertilizers are natural fertilizers containing living microorganisms that promote plant growth by increasing the availability of essential nutrients in the soil. They play a vital role in sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil fertility, reducing dependency on chemical fertilizers, and minimizing environmental degradation.

1. Benefits of Using Biofertilizers
a. Eco-Friendly and Sustainable
- Natural Origin: Biofertilizers are derived from naturally occurring microorganisms, ensuring minimal environmental harm.
- Biodegradable: They decompose in the soil without leaving harmful residues.
- Reduced Pollution: They prevent soil, water, and air pollution caused by excessive chemical fertilizer use.
b. Enhances Soil Fertility
- Microorganisms in biofertilizers improve the nutrient content and organic matter in soil.
- Nitrogen Fixation: Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Azospirillum convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can absorb.
- Phosphorus Solubilization: Microbes like Pseudomonas and Bacillus solubilize insoluble phosphates, making them available to plants.
- Potassium Mobilization: Potassium-solubilizing bacteria enhance potassium availability.
c. Cost-Effective
- Biofertilizers are less expensive than chemical fertilizers.
- They reduce the need for synthetic inputs, lowering overall agricultural costs.
d. Improves Soil Structure and Health
- Promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
- Enhances soil aeration and water retention by improving soil structure.
- Reduces the risk of soil degradation and erosion.
e. Increases Crop Yield and Quality
- Encourages root development and better nutrient uptake.
- Results in healthier plants with improved yields and nutritional content.
2. Role in Sustainable Agriculture
- Supports Organic Farming: Essential for organic farming practices, ensuring compliance with eco-friendly standards.
- Mitigates Climate Change: Reduces greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing the production and use of synthetic fertilizers.
- Promotes Biodiversity: Encourages a thriving microbial ecosystem, enhancing overall soil biodiversity.
3. Types of Biofertilizers
- Nitrogen-Fixing Biofertilizers: Rhizobium, Azospirillum, and Azotobacter.
- Phosphate-Solubilizing Biofertilizers: Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Aspergillus.
- Potassium-Solubilizing Biofertilizers: Frateuria.
- Mycorrhizal Biofertilizers: Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), which enhance water and nutrient uptake.
- Cyanobacteria: Blue-green algae like Anabaena and Nostoc for nitrogen fixation in rice paddies.
4. Challenges with Biofertilizers
- Slow Action: Effects may take time compared to chemical fertilizers.
- Storage and Shelf Life: Require specific storage conditions to maintain viability.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Sensitive to temperature, humidity, and pH changes.
- Awareness and Adoption: Limited knowledge among farmers about their benefits and application methods.
Biofertilizers are indispensable for achieving sustainable agricultural practices and meeting global food demands while preserving environmental health. Their ability to enhance soil fertility, reduce chemical dependency, and promote long-term productivity makes them a key component of future farming systems.