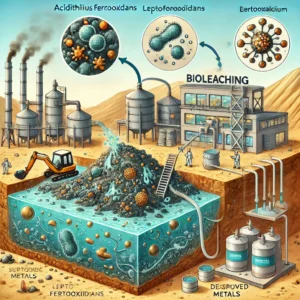
Bio-mining refers to the use of microorganisms, such as bacteria or archaea, to extract metals and other valuable materials from ores, mining waste, or industrial waste. It is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional mining techniques, as it minimizes the need for hazardous chemicals and reduces the environmental impact associated with conventional mining processes.

Key Aspects of Bio-mining:
Mechanism:
- Microorganisms secrete organic acids or other compounds that solubilize metals from ores or waste.
- Bioleaching and bio-oxidation are the two main processes used in bio-mining:
- Bioleaching: Involves the extraction of metals by converting them into a soluble form.
- Bio-oxidation: Used to make the metals more accessible by breaking down surrounding minerals.
Applications:
- Metal Recovery: Extraction of metals like copper, gold, nickel, cobalt, and zinc.
- Waste Management: Processing of mining waste, e-waste, or industrial waste to recover valuable metals.
- Environmental Remediation: Detoxification of contaminated environments, including acid mine drainage.
Microorganisms Involved:
- Examples include Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and Sulfolobus species. These microbes thrive in acidic conditions and are highly efficient in metal solubilization.
Advantages:
- Eco-friendly compared to chemical-based extraction methods.
- Operates under ambient temperature and pressure, reducing energy consumption.
- Utilizes low-grade ores, which are often left unexploited in traditional mining.
Challenges:
- Bio-mining processes are slower than conventional methods.
- Requires specific conditions, such as a controlled pH, temperature, and nutrient availability, for optimal microbial activity.
- Not suitable for all types of ores.
Example:
- Gold Extraction: In bio-oxidation, bacteria are used to break down sulfide minerals in gold ore, releasing the gold for further processing.
- Copper Recovery: Bioleaching of low-grade copper ore using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is widely practiced.
Bio-mining is gaining popularity due to its sustainability and potential to make use of waste resources while reducing environmental harm.
Advantages of Bio-mining
Bio-mining offers several benefits compared to traditional mining methods. Its sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and minimal environmental impact make it a promising technology for the extraction of metals and waste management. Below are the key advantages:
1. Eco-friendly Process
- Reduced Chemical Usage: Unlike traditional mining, bio-mining does not rely on harsh chemicals such as cyanide or sulfuric acid, minimizing toxic waste.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Bio-mining processes occur at ambient temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Environmental Remediation: Microbes can clean up contaminated sites by breaking down pollutants and heavy metals, aiding in environmental restoration.
2. Cost-effectiveness
- Low Operational Costs: Bio-mining requires less energy and fewer resources compared to traditional mining processes.
- Utilization of Low-grade Ores: It allows the extraction of metals from ores with low mineral content, which are often discarded in conventional mining.
- Waste Recovery: Valuable metals can be extracted from mining waste, reducing the need for new mining operations.
3. Sustainability
- Resource Efficiency: Bio-mining promotes the efficient use of natural resources, enabling the recycling of metals from e-waste, tailings, and industrial byproducts.
- Renewable Resource Use: The microorganisms used in bio-mining are naturally occurring and self-sustaining under the right conditions.
4. Reduced Environmental Impact
- Minimal Land Disturbance: Bio-mining requires smaller operational sites, reducing habitat destruction and deforestation.
- Reduced Water Pollution: By limiting the use of harmful chemicals, bio-mining decreases the risk of water contamination.
- Mitigation of Acid Mine Drainage: Certain microbes can neutralize acidic conditions in mining areas, reducing environmental harm.
5. Flexibility
- Wide Range of Applications: Bio-mining can be applied to various types of ores, including sulfide ores and e-waste, making it versatile for different industries.
- Scalability: The technology can be adapted for small-scale operations or large-scale industrial applications.
6. Improved Metal Recovery
- Selective Metal Extraction: Microorganisms can target specific metals, improving the efficiency and purity of the extracted materials.
- Processing Complex Ores: Bio-mining can extract metals from ores that are difficult to process using conventional methods.
Examples of Advantages in Practice
- Copper Recovery: Large-scale bioleaching operations, such as those in Chile, have proven that bio-mining is economically and environmentally viable for copper extraction.
- Gold Extraction: Bio-oxidation techniques are used to increase the recovery of gold from refractory ores.
Overall, the advantages of bio-mining lie in its ability to combine environmental sustainability with economic feasibility, making it an increasingly attractive alternative in the mining industry.